Holter Monitoring
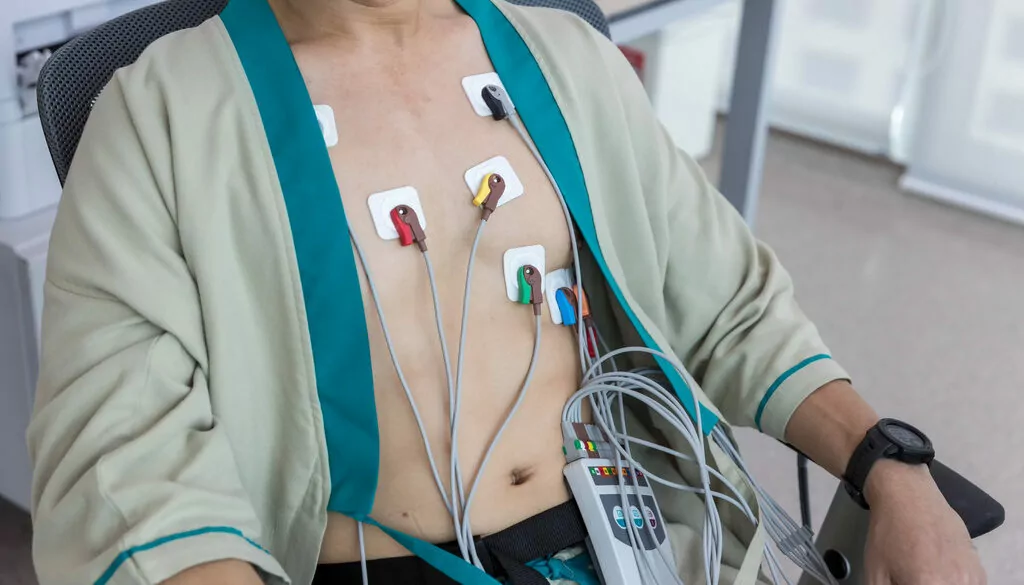
Holter Monitoring
Holter monitoring is a diagnostic procedure used to monitor and record the electrical activity of the heart over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. This non-invasive test helps healthcare providers evaluate cardiac rhythms and detect abnormalities that may not be captured during a standard electrocardiogram (ECG).
How it Works
During Holter monitoring, small electrodes (sticky patches) are placed on the chest, which are connected to a portable Holter monitor device. The device continuously records the heart's electrical signals (ECG) as the patient goes about their daily activities, providing a comprehensive view of cardiac activity over a prolonged period. Patients are instructed to keep a diary of activities and symptoms, noting any symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or chest pain during the monitoring period.
Clinical Applications
Diagnosis of Arrhythmias:
Holter monitoring is essential for diagnosing various types of arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, tachycardia, and other irregular heart rhythms. It captures intermittent or transient arrhythmias that may not be detected during a standard ECG.
Assessment of Symptoms:
It helps correlate symptoms such as palpitations, fainting episodes, and chest pain with specific cardiac events, providing valuable information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy:
Holter monitoring is used to assess the effectiveness of anti-arrhythmic medications, pacemakers, or other interventions aimed at managing cardiac rhythm disorders. It helps healthcare providers adjust treatment plans based on real-time data.
Evaluation of Silent Ischemia:
In patients with suspected coronary artery disease, Holter monitoring can detect silent ischemia (lack of oxygen-rich blood flow to the heart muscle) by monitoring changes in the ST segment of the ECG during daily activities.
Risk Assessment:
It aids in assessing the risk of sudden cardiac death or other cardiovascular events in patients with known heart conditions or risk factors.
